Setup environment for testnet/mainnet
In the previous chapters, we used a local blockchain emulator where a very simple wallet was already deployed, which can only send coins to a certain address in order to deploy a contract via an external message.
For the test/main network, you need to have an already deployed wallet (giver). We will use the EverWallet as the giver.
A wallet can be created programmatically using tonos-cli, eversdk or inpage-provider.
But we will use a browser extension, EverWallet, for this purpose. We will need it anyway for writing the frontend or for interacting with contracts through a web interface.
Install EverWallet in the Chrome browser and create a new wallet there. At this stage, you should not have any problems. Write down the seed phrase and by default, an EverWallet will be created for you using the pair of keys obtained from the seed phrase. Never share your seed phrase or private key with anyone, and do not commit it in the git. Keep it in a safe place, because if you lose access to your seed phrase or private key, you will also lose access to your wallet and all the assets it contains.
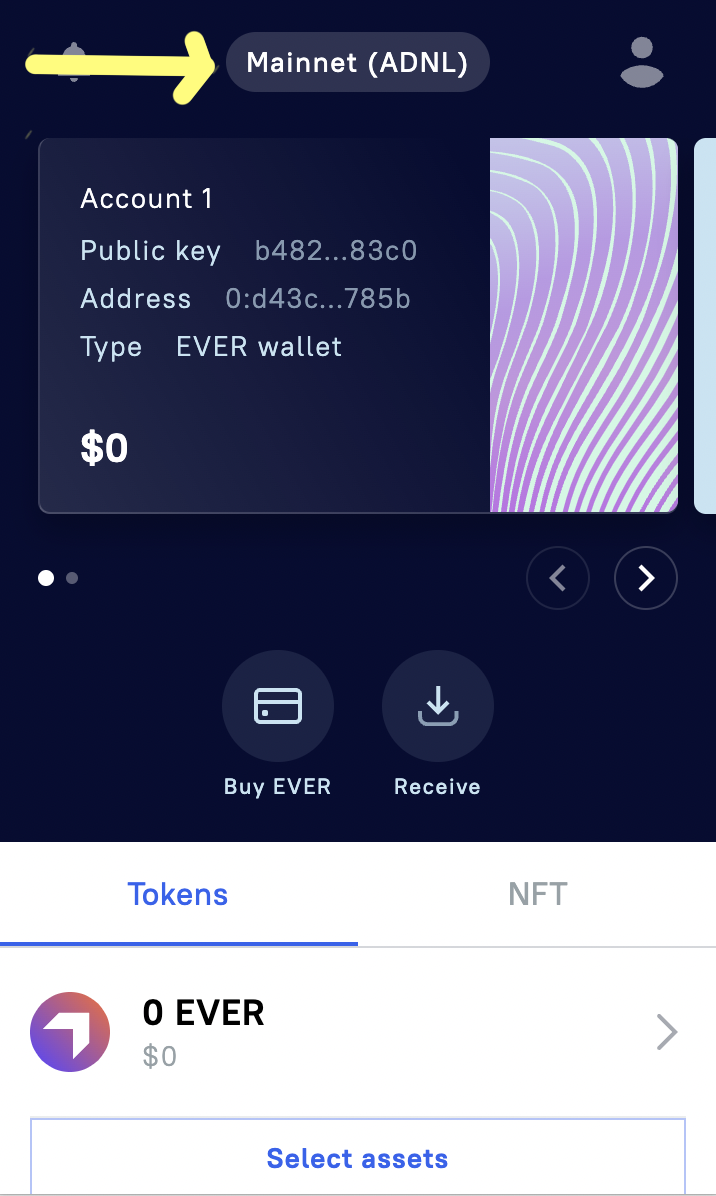
After creating a wallet on the main page of the extension, your wallet is shown, its address and public key, and a
toggle switch between networks at the top. There you can choose Mainnet (adnl\gql - just different types of endpoint),
several test networks (we are only interested in testnet), and a local node. We need to choose Testnet.
To get GraphQL endpoints for testnet/mainnet, you need to register at evercloud.dev. There, you need to create a project, and next to your endpoints, there is a faucet icon, which is a button to get test tokens.
How to get coins in the mainnet:
There are two ways to get tokens to your wallet in the main network. The first is simply to buy on a centralized exchange and withdraw to your address, and the second is to use Octus Bridge. When transferring USDT, USDC, DAI from connected EVM networks, you need to enable 'Pay gas fees in USDT tokens', and specify how much USDT to exchange for EVER, and after the transfer the bridge will exchange this amount on AMM (flatqube) and send you native coins to your wallet.After receiving the coins, you need to make a transfer to deploy the wallet, for example, send 1 ever to yourself.
Now we have a test wallet that can be used as both a wallet and a giver. Let's see how to set up the test network in our examples:
// For the testnet we need to change params of ProviderRpcClient for
const DEV_NET_NETWORK_ENDPOINT = 'https://devnet-sandbox.evercloud.dev/graphql';
const ever = new ProviderRpcClient({
fallback: () =>
EverscaleStandaloneClient.create({
connection: {
id: 1,
type: "graphql",
group: "dev",
data: {
endpoints: [DEV_NET_NETWORK_ENDPOINT],
latencyDetectionInterval: 1000,
local: false,
},
},
keystore: keyStore,
accountsStorage: accountStorage
}),
});
// Pay attention we set public avaiable endpoint devnet-sandbox.evercloud.dev with
// low rate limits and sla. You can create private endpoint for free by using
// https://dashboard.evercloud.dev/
// For the mainnet
const MAIN_NET_NETWORK_ENDPOINT = 'Create there https://dashboard.evercloud.dev/';
const ever = new ProviderRpcClient({
fallback: () =>
EverscaleStandaloneClient.create({
connection: {
id: 1,
type: "graphql",
group: "main",
data: {
endpoints: [MAIN_NET_NETWORK_ENDPOINT],
latencyDetectionInterval: 1000,
local: false,
},
},
keystore: keyStore,
accountsStorage: accountStorage
}),
});
// We have changed the network settings, now let's configure the wallet to be a giver.
// You need to install evescale-crypto package
// npm i everscale-crypto
// To obtain the keypair from the seed phrase
// Change giver.js script from our exemples (basic, use_wallets, simple-tip3),
// https://github.com/mnill/everscale-crash-course-snippets
// in which the test giver for the local node was configured, to the following code:
const {EverWalletAccount} = require("everscale-standalone-client/nodejs");
const { deriveBip39Phrase } = require("everscale-crypto");
const {Address} = require("everscale-inpage-provider");
// address of our EverWallet ( taken from the extension )
const address = new Address('0:2746d46337aa25d790c97f1aefb01a5de48cc1315b41a4f32753146a1e1aeb7d');
// Never commit your seed phrase to the repository
const seed = 'action inject penalty envelope rabbit element slim tornado dinner pizza off blood';
// Path to derive a keypair from the seed phrase.
// The last /0 is key index, you can modify it if you need to derive
// more than one keypair from one seed.
const path = "m/44'/396'/0'/0/0";
// Obtain keypair from the seed
const keypair = deriveBip39Phrase(seed, path);
// Ever wallet abi
const broxusEverWalletAbi = {
"ABI version": 2,
version: "2.3",
header: ["pubkey", "time", "expire"],
functions: [
{
name: "sendTransaction",
inputs: [
{ name: "dest", type: "address" },
{ name: "value", type: "uint128" },
{ name: "bounce", type: "bool" },
{ name: "flags", type: "uint8" },
{ name: "payload", type: "cell" },
],
outputs: [],
},
],
events: [],
};
// This function used in test.js to add
// keypair to the keystore
function getGiverKeypair() {
return keypair;
}
// Send value coins to the address(sendTo)
async function getTokensFromGiver(everProvider, sendTo, value) {
const giver = new everProvider.Contract(broxusEverWalletAbi, address);
const {transaction} = await giver.methods.sendTransaction({
value: value,
dest: sendTo,
bounce: false, // left money on the target contract
flags: 3, // 1 + 2 pay fee from the wallet account and ignore errors
payload: "",
}).sendExternal({
// inpage-provider will search the keypair for this pubkey
// in the keyStore. We use getGiverKeypair method in test.js
// to add the keys to the keyStore.
publicKey: keypair.publicKey
});
if (transaction.aborted) {
throw new Error(`Transaction aborted with code ${transaction.exitCode}`)
}
}
module.exports = { getGiverKeypair, getTokensFromGiver };
// Now we can use testnet. If your transaction is
// crashing by timeout on `getTokensFromGiver` - most probably your
// wallet is not deployed. Just sent 1 ever to yourself via the extension to deploy it.I also remind you of the standard hygiene rules when working with testnet/mainnet:
- Use different wallets for different networks (test/main/local), make sure you don't accidentally leak seed phrases into git.
- Use different wallets for different projects.
- After successfully deploying contracts to the mainnet, always transfer its ownership to an address that has never been used in scripts. It's better if this is a multisig or hardware wallet.